
Project Overview
As a key AI application within the financial sector, CTBC AI Voice Risk Management utilizes ASR technology to digitize and evaluate physical bank transactions. By analyzing these recordings, the system automatically assesses transaction risks and monitors frontline staff behavior. Our goal was to create a safety net that detects excessive commitments or misleading sales tactics, ensuring that every customer interaction remains transparent and aligned with their actual financial needs.
Information
Product:CTBC AI Voice Risk Management
Issuing Company:CTBC Bank
Platform:Offline service
Preface
In late 2023, following the group's strategic focus on AI integration, I was appointed to the Consumer AI Applications Department. Having previously led numerous process improvement initiatives and research projects for branch operations, I sought to bridge the gap between front-line needs and advanced technology. My goal has been to leverage these deep operational insights to develop AI-driven tools that deliver tangible impact and streamline the customer experience.
Pain Points
Historically, physical bank transactions have been prone to various disputes due to a lack of objective records. Common pain points include inexperienced staff using imprecise terminology, leading to customer misunderstandings. Furthermore, post-purchase regrets often escalate into formal complaints—most notably in cases where senior citizens purchase insurance products, and their family members later allege 'misleading sales tactics' or 'inducement.' Without a transparent audit trail, these consumer disputes are difficult to resolve and can damage the bank's reputation.
Solution
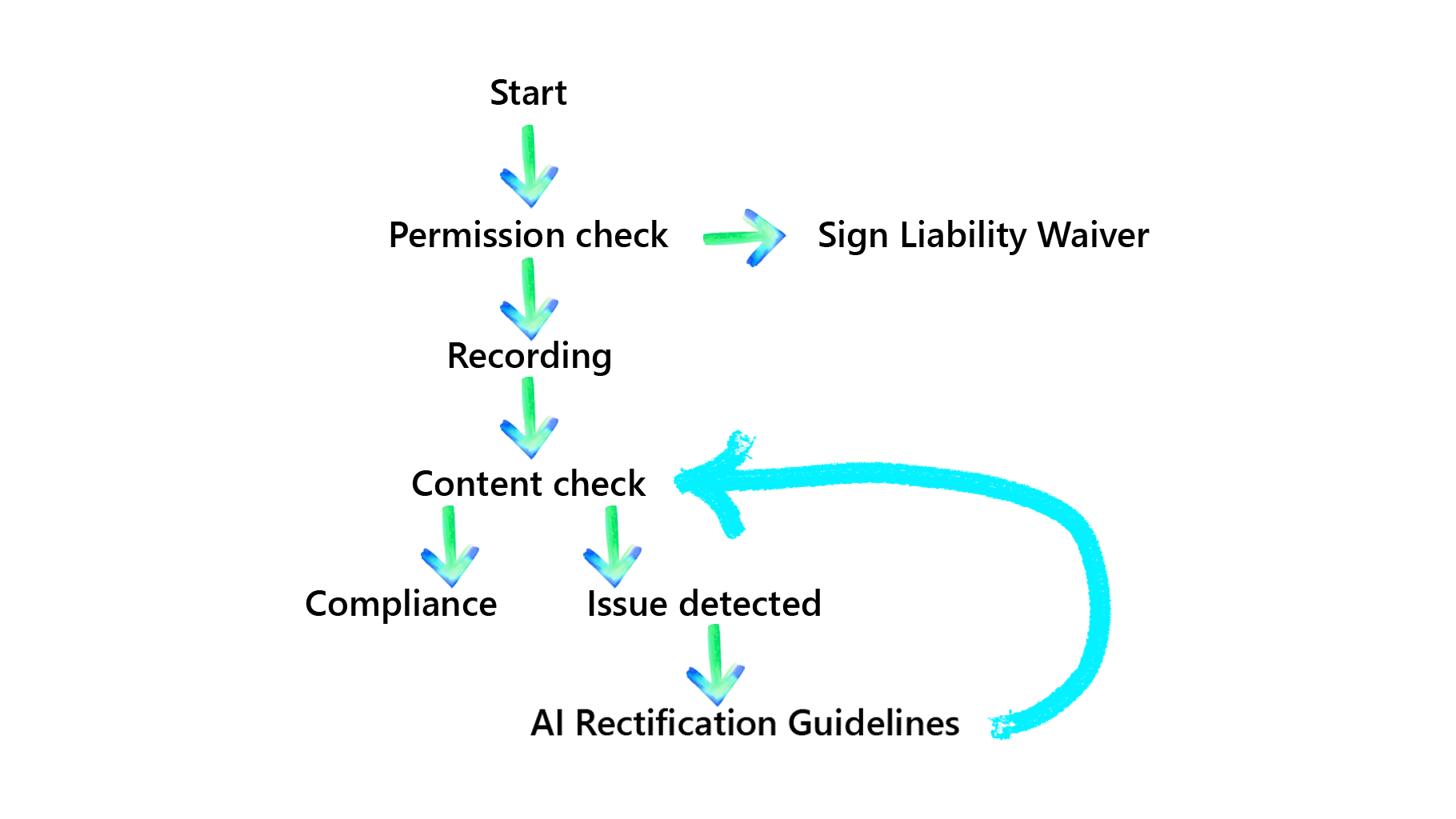
To address these challenges, we designed an AI-driven auditing agent that monitors and records the full transaction process upon customer approval. More than just a recording tool, the AI acts as a real-time advisor: when a flaw is identified, the system instantly notifies the banker and offers actionable remediation steps. This proactive approach allows staff to correct errors during the session, ensuring a transparent and compliant experience for the customer.
Challenges
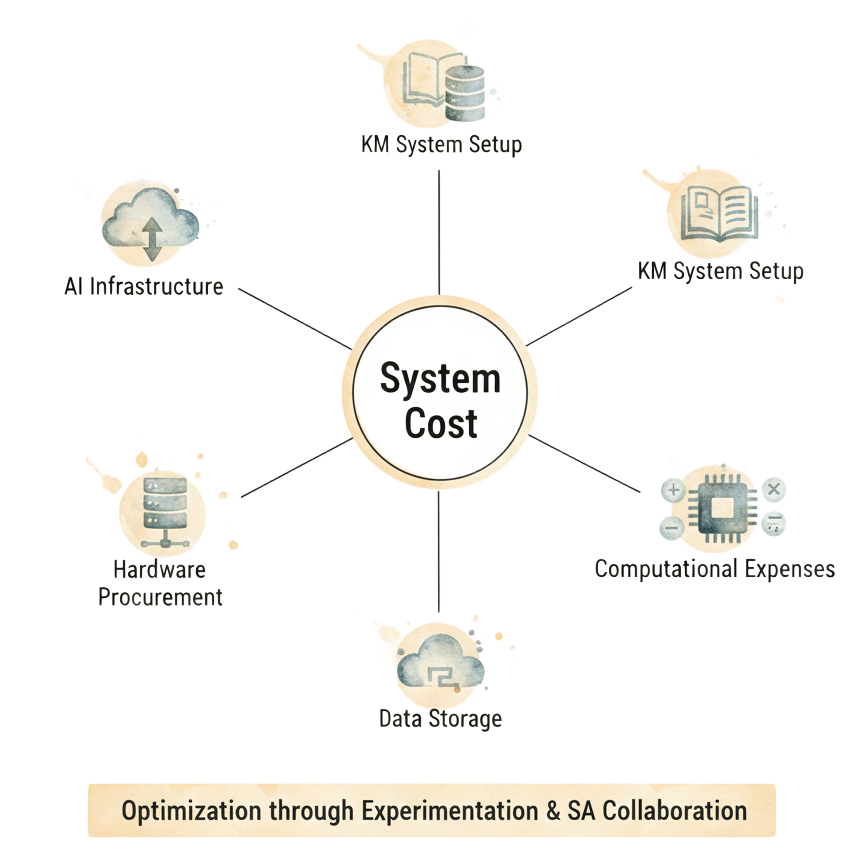
This project subsequently faced two pivotal challenges: user adoption and cost efficiency. The primary hurdle was addressing user willingness – despite the clear benefits in mitigating transaction risks, frontline bankers naturally exhibited reluctance towards real-time monitoring. Our strategy was therefore centered on designing a positive feedback mechanism and explicitly ensuring the system would not directly impact individual performance reviews or become a punitive tool. This required careful UX/UI design to transform the AI from a 'monitor' into a 'supportive assistant.'
The second critical challenge revolved around cost management. Ensuring the system remained within an acceptable budget while delivering high performance was a significant undertaking. This encompassed meticulous planning for AI infrastructure, hardware procurement, data storage, and computational expenses. Furthermore, the establishment and integration of Knowledge Management (KM) systems for shared learnings required extensive experimentation and cross-departmental System Architect (SA) discussions to optimize for both functionality and cost-effectiveness.
Lessons Learned
Although the project was still in the validation phase when I concluded my tenure, it provided a profound lesson on the realities of corporate AI integration. The primary obstacle to AI adoption in a large-scale enterprise is seldom the technology itself; rather, it is the intricate web of stakeholders and the constant pressure to demonstrate immediate, tangible business value. Success in this environment requires more than technical excellence—it demands the ability to navigate complex organizational interests and align them with a clear path to profitability.